String Operations in Python
In this post, we’ll explore how strings work in Python. Strings are one of the essential data types and are used to represent text. We’ll look at how to create strings, concatenate them, access specific characters, and learn about various built-in methods that can be used to manipulate strings.
Creating Strings in Python
Strings in Python can be created by enclosing text within single quotes ('), double quotes ("), or triple quotes (''' or """). Here are some examples:
1
2
3
4
5
string1 = 'Hello, world!'
string2 = "Welcome to Python"
string3 = "This string contains a 'single quote'"
string4 = 'This string contains a "double quote"'
string5 = "This string contains an escaped \"double quote\""
string1: Created with single quotes. You can include double quotes inside without escaping them.string2: Created with double quotes, allowing single quotes without escaping.string3: Contains a single quote, enclosed with double quotes.string4: Contains a double quote, enclosed with single quotes.string5: Contains an escaped double quote using\.
Here is how these strings can be printed:
1
2
3
4
5
print(string1) # Output: Hello, world!
print(string2) # Output: Welcome to Python
print(string3) # Output: This string contains a 'single quote'
print(string4) # Output: This string contains a "double quote"
print(string5) # Output: This string contains an "double quote"
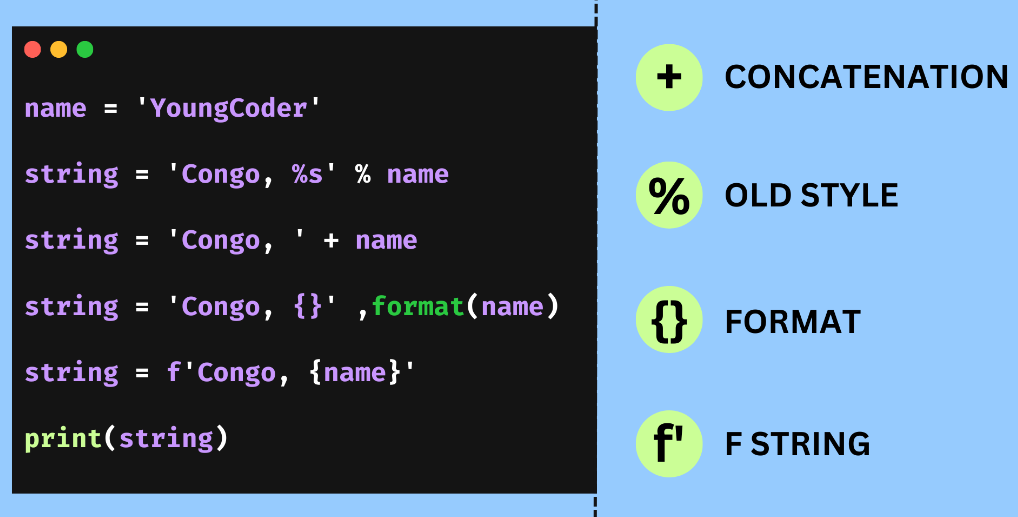
Concatenating Strings in Python
String concatenation refers to the operation of joining two or more strings into one. This can be done using the + operator:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
string1 = 'Hello, world!'
string2 = "Welcome to Python"
number1 = 5
print(string1 + string2) # Output: Hello, world!Welcome to Python
print(string1 + ' ' + string2) # Output: Hello, world! Welcome to Python
print(string1 * 3) # Output: Hello, world!Hello, world!Hello, world!
print(str(number1) + string1) # Output: 5Hello, world!
- Concatenation with
+: Joinsstring1andstring2. - Including a Space: Adding
' 'between strings to create separation. - Repetition with
*: Repeatsstring1three times. - Concatenation with a Number: Convert the number to a string with
str()before concatenating.
Length of a String
To get the length of a string, use the len() function, which counts the total number of characters including spaces:
1
2
3
string = "This is a sample string for length calculation."
print(len(string)) # Output: 47
You can also calculate the length of a substring:
1
print(len(string[0:15])) # Output: 15
Accessing Characters in a String
In Python, you can access individual characters of a string using indexing, where the first character has index 0:
1
2
3
4
5
string = "Python is amazing"
print(string[0]) # Output: P
print(string[7]) # Output: i
print(string[-1]) # Output: g
- Positive Indexing: Starts from the beginning (
0is the first character). - Negative Indexing: Starts from the end (
-1is the last character).
You can also get a substring using slicing:
1
print(string[0:6]) # Output: Python
String Methods in Python
Strings in Python come with a variety of built-in methods that allow you to manipulate them in different ways:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
string = 'Python is awesome'
print(string.upper()) # Output: PYTHON IS AWESOME
print(string.lower()) # Output: python is awesome
print(string.capitalize()) # Output: Python is awesome
print(string.title()) # Output: Python Is Awesome
print(string.replace('awesome', 'incredible')) # Output: Python is incredible
print(string.count('o')) # Output: 2
print(string.find('is')) # Output: 7
upper(): Converts all characters to uppercase.lower(): Converts all characters to lowercase.capitalize(): Capitalizes the first character.title(): Capitalizes the first character of each word.replace(old, new): Replaces all occurrences ofoldwithnew.count(substring): Counts how oftensubstringappears in the string.find(substring): Finds the first occurrence ofsubstring.
Practice Exercises
Try the following exercises to reinforce what you have learned:
Exercise 1
Create a program with a variable containing the string “I love my dog; it’s the best” and display the following:
- Print the first two characters.
- Print the last three characters.
- Print every second character in the string.
- Print the string in reverse order.
- Print the string in normal and reverse order, combined.
Exercise 2
Create a program that takes the string “Apart” and inserts a dot (.) between each character, resulting in “A.p.a.r.t”.
More Information
Understanding strings is a fundamental aspect of Python programming. They are used extensively in almost every program and mastering string manipulation can greatly enhance your coding skills. For more detailed information, consider exploring:
Next Steps: In the next post, we’ll continue our journey by looking at user input and output in Python. Stay tuned and happy coding!