Public Cloud vs. Private Cloud - Understanding Key Differences and Strategic Value
As organizations increasingly rely on cloud solutions, choosing the right cloud deployment model is crucial. While public clouds offer scalability and cost-effectiveness, private clouds provide enhanced control and data security. This post explores the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats (SWOT) of public clouds, followed by a comparison between public and private cloud models to help businesses determine the best fit for their needs.
Public Cloud SWOT Analysis
The SWOT analysis highlights the core strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats associated with the public cloud model, providing a strategic overview for organizations considering this deployment model.
| Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|
| - High availability and reliability | - Limited control over legal and regulatory compliance |
| - Elasticity and scalability | - Minimal control over supply chain processes |
| - Simplified patch management | - Limited logging capabilities for incident response |
| - Consistent response times | - Regional data regulations and restrictions |
| - Business continuity and disaster recovery | - Risk of performance deterioration from poor network quality |
| - Physical security measures | - Data transfer challenges between providers |
| Opportunities | Threats |
|---|---|
| - Ability to provide risk analysis and security monitoring | - Attractiveness to cyber attackers due to large data volumes |
| - Potential to offer real-time security supervision | - High impact of attacks if security measures fail |
| - Development of security-focused services | - Threat of information leakage from user isolation failures |
| - Alignment with growing compliance needs | - Dependence on provider for data control |
| - Possible provider lock-in when switching services |
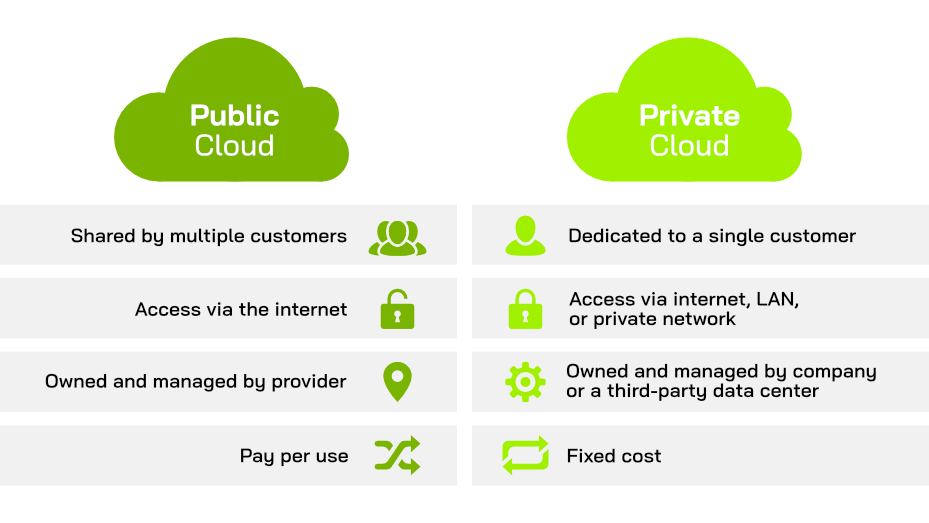
Public Cloud vs. Private Cloud: A Comparison
The following table compares the key characteristics of public and private clouds, helping businesses identify the optimal solution based on their security needs, resource management preferences, and budget.
| Feature | Public Cloud | Private Cloud |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Shared cloud environment accessible over the internet | Exclusive cloud environment for a single organization |
| Cost | Lower initial costs; pay-as-you-go model | Higher upfront costs; customizable resource investment |
| Scalability | High, with virtually unlimited scalability | Limited by on-premises infrastructure capacity |
| Security | Managed by the provider; offers encryption and access controls | Enhanced control; in-house or managed security |
| Data Control | Limited by provider; data resides in shared infrastructure | Complete control; organization manages data and access |
| Maintenance | Managed by cloud provider | Requires in-house or managed IT resources |
| Compliance | Varies by provider; suitable for general data | Suitable for organizations with strict compliance needs |
| Best For | Cost-sensitive applications, software development | Sensitive data management, regulated industries |
Key Insights
- Public Cloud: Ideal for companies looking to reduce costs and benefit from scalable resources. Best suited for non-sensitive data and applications requiring rapid deployment.
- Private Cloud: Best for organizations needing maximum control over data security and compliance. Often chosen by regulated industries that require dedicated resources within a secure environment.
Hybrid Cloud Consideration
For businesses requiring both scalability and control, a hybrid cloud model combines the strengths of public and private clouds, enabling secure storage for sensitive data and scalable public resources for less sensitive applications.
Choosing between public and private clouds depends on an organization’s priorities for security, cost, and scalability. The public cloud model offers affordability and flexibility, while private clouds provide enhanced control and compliance. By understanding the SWOT of public clouds and comparing both models, businesses can make strategic decisions that align with their unique operational needs and data security requirements. As the cloud landscape evolves, hybrid models also offer viable solutions for organizations seeking a balance between cost-efficiency and data control.