Boolean, Relational, and Logical Operators in Python
In this post, we’ll explore the fundamentals of Boolean data types, relational operators, and logical operators in Python. You will learn how to use them to compare values, combine conditions, and make decisions in your programs. Additionally, we’ll discuss some built-in Boolean methods for strings in Python.
What are Boolean Values in Python?
Booleans are a data type in Python that can have one of two values: True or False. They are especially useful for comparisons and decision-making in programs.
Here’s an example:
1
2
3
4
is_student = True # The variable is assigned a boolean value of True
is_working = False # The variable is assigned a boolean value of False
print(type(is_student)) # Output: <class 'bool'>
Boolean values can also be the result of comparisons or functions that evaluate certain conditions:
1
2
3
4
5
empty_string = "" # Evaluates to False
filled_string = "Hello" # Evaluates to True
print(bool(empty_string)) # Output: False
print(bool(filled_string)) # Output: True
Booleans are fundamental in programming, allowing us to control the flow of our programs through decision-making and loops.
Relational Operators in Python
Relational operators, also known as comparison operators, are used to compare two values. They return a boolean value (True or False) depending on whether the comparison is true or false. Python provides the following relational operators:
==: Checks if two values are equal.!=: Checks if two values are not equal.>: Checks if the left value is greater than the right.<: Checks if the left value is less than the right.>=: Checks if the left value is greater than or equal to the right.<=: Checks if the left value is less than or equal to the right.
Here’s an example of how to use these operators:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
a = 10
b = 20
print(a == b) # Output: False
print(a != b) # Output: True
print(a > b) # Output: False
print(a < b) # Output: True
print(a >= b) # Output: False
print(a <= b) # Output: True
Relational operators allow us to create conditions that can be used in decision-making structures, like if statements.
Example: Comparing User Input Values
Here’s a simple program that takes user input and compares two numbers:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
num1 = int(input("Enter a number: "))
num2 = int(input("Enter another number: "))
print(num1 > num2) # Checks if num1 is greater than num2
print(num1 < num2) # Checks if num1 is less than num2
print(num1 == num2) # Checks if num1 is equal to num2
print(num1 != num2) # Checks if num1 is not equal to num2
This program uses relational operators to evaluate the relationship between two user-provided numbers.
Logical Operators in Python
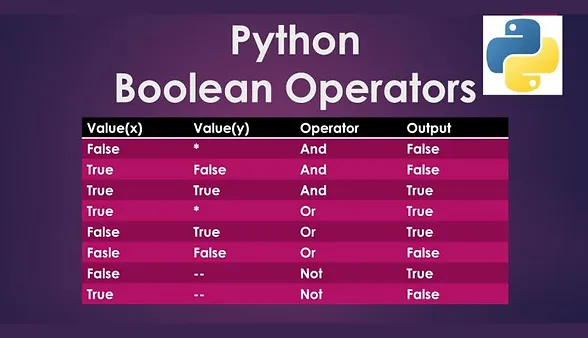
Logical operators in Python are used to combine multiple conditions. Python provides three logical operators: and, or, and not.
and: ReturnsTrueif both conditions areTrue.or: ReturnsTrueif at least one condition isTrue.not: Inverts the result, returningTrueif the condition isFalse.
Here’s how you use them:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
a = 10
b = 20
c = 30
# Example of 'and'
print(a < b and b < c) # Output: True
# Example of 'or'
print(a > b or b < c) # Output: True
# Example of 'not'
print(not(a > b)) # Output: True
Logical operators allow you to combine multiple relational conditions to form complex decision criteria in your programs.
Example: Combining Conditions
Here’s an example of using logical operators to combine conditions:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
x = 10
y = 5
z = 15
print(x > y and y < z) # Output: True
print(x == 10 or y > 10) # Output: True
print(not(z < y)) # Output: True
In this example, logical operators allow us to evaluate multiple conditions and determine if they collectively meet certain criteria.
Boolean Methods for Strings
Python provides several built-in Boolean methods for strings that return True or False based on the characteristics of the string. Here are some commonly used Boolean methods:
startswith(substring): ReturnsTrueif the string starts with the specified substring.endswith(substring): ReturnsTrueif the string ends with the specified substring.isalnum(): ReturnsTrueif all characters are alphanumeric (letters or numbers).isalpha(): ReturnsTrueif all characters are alphabetic.isdigit(): ReturnsTrueif all characters are digits.islower(): ReturnsTrueif all characters are in lowercase.isupper(): ReturnsTrueif all characters are in uppercase.
Here’s an example of how to use these methods:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
string1 = 'Hello World'
string2 = '12345'
print(string1.startswith('Hello')) # Output: True
print(string1.endswith('World')) # Output: True
print(string2.isdigit()) # Output: True
print(string1.isalpha()) # Output: False
These Boolean methods are useful for quickly checking certain conditions of strings in your programs.
Practice Exercises
Try the following exercises to reinforce what you’ve learned:
Exercise 1: Comparisons
Write a program that takes user input for two numbers and checks if they are equal, greater, or less using relational operators.
Exercise 2: Logical Operator Practice
Write a program that takes three boolean values and evaluates different logical combinations using and, or, and not.
Exercise 3: String Analysis
Write a program that takes a string input from the user and checks if the string starts with a certain word, ends with another, and whether it is entirely alphanumeric.
More Information
Boolean values and logical operations are essential parts of programming. They form the backbone of decision-making and control flow in any program. Understanding these concepts thoroughly will greatly enhance your coding skills.
For further reading:
- Python Official Documentation on Boolean Operations
- Real Python - Understanding Boolean Logic in Python
Next Steps: In the next post, we’ll explore Loops in Python - While, For, Range, and Control Statements in Python. Continue practicing and honing your skills!