A Comprehensive Guide to Managing and Monitoring AWS Free Tier Services
The AWS Free Tier is a great way for users, whether they are developers, small business owners, or large enterprises, to get hands-on experience with AWS cloud services without any initial financial commitment. However, effectively managing and monitoring these services is essential to avoid unexpected costs once the free tier limits are exceeded. This blog post provides an extensive exploration of AWS Free Tier offerings, including managing service usage, monitoring through AWS tools, and tips for transitioning from free to paid services. We’ll also examine how a DevOps engineer or programmer can leverage these offerings to maintain efficient cloud operations.
Understanding AWS Free Tier Offerings
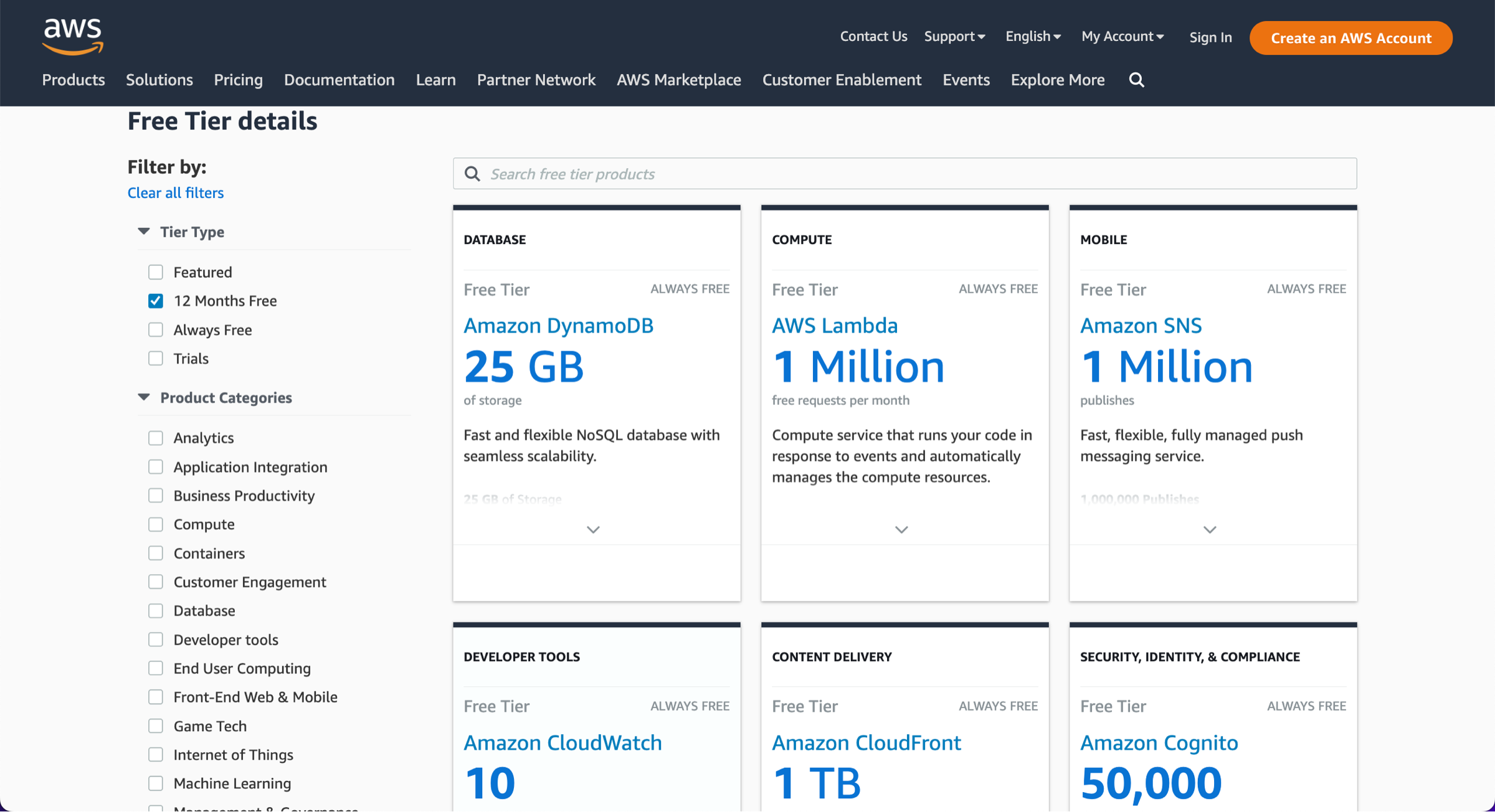
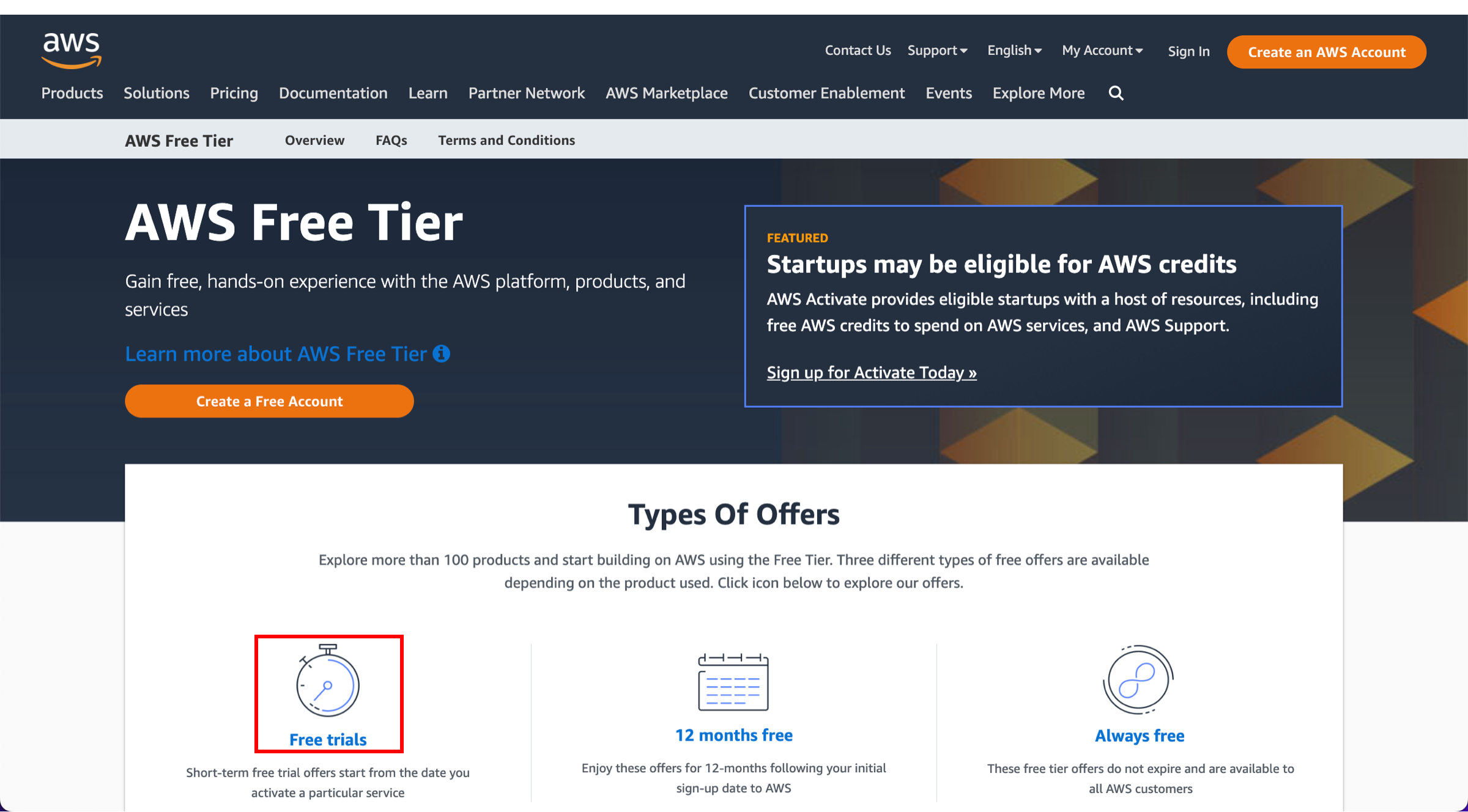
The AWS Free Tier provides access to over 100 AWS services free of charge for a specified period or usage limit. These offerings can be divided into three main types: short-term free trials, 12-month free offerings, and always-free services. Understanding these categories helps users better utilize AWS services based on their needs.
- Short-term Free Trials: These offers are valid for a limited time, such as 30 or 60 days, and begin from the activation of the service. For instance, some AI and machine learning services fall under this category.
- 12-Month Free Offers: These services are available to new AWS customers for up to 12 months from the sign-up date. Examples include 750 hours of Amazon EC2 micro instance usage per month and 5 GB of Amazon S3 storage.
- Always Free: Some services remain free forever, up to specific usage limits, as long as you have a valid AWS account. For instance, AWS Lambda offers 1 million free requests per month.
Knowing the different types of offerings is crucial to avoid incurring costs once the free limits are exceeded. To explore services and their respective free tier eligibility, always start at the AWS Free Tier homepage. Here you can filter services by offering type or category, helping you make informed decisions.
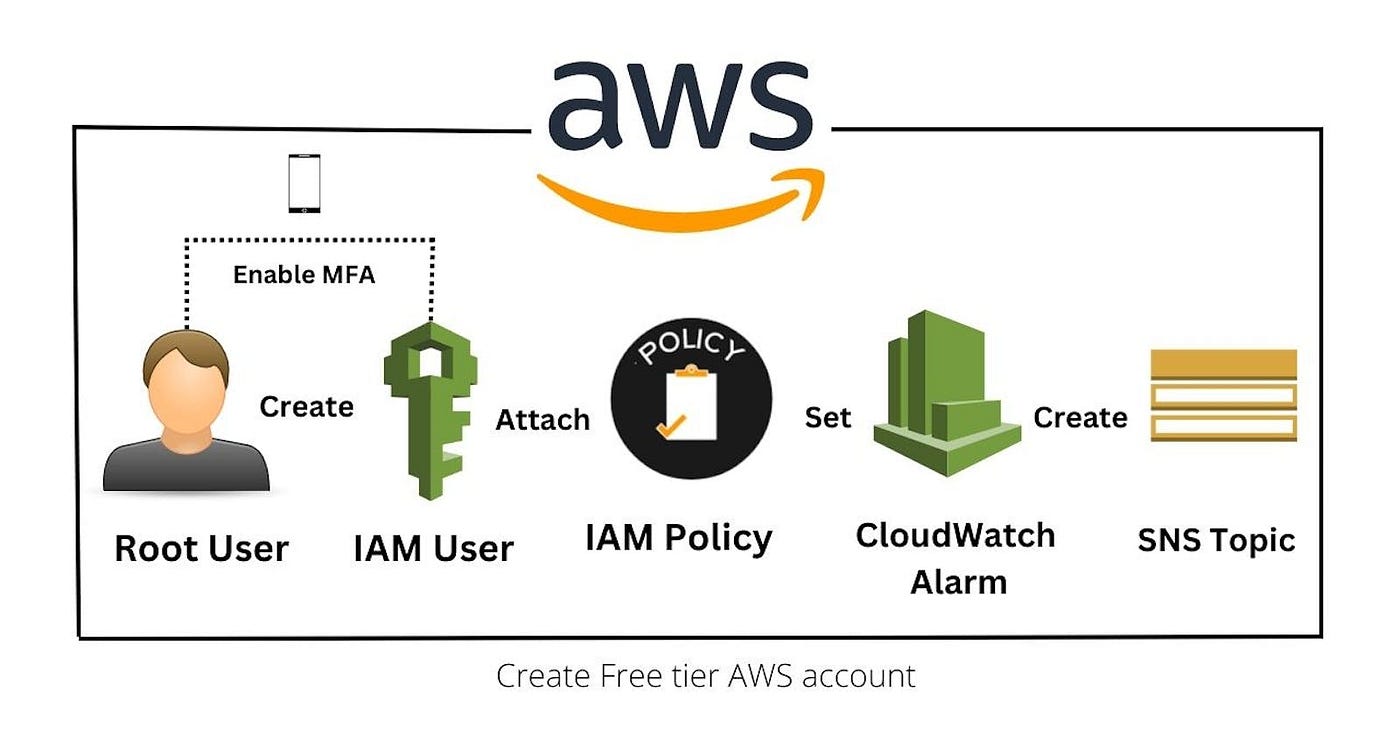
AWS Free Tier Introduction to Offerings
Managing AWS Free Tier Services
Managing AWS services effectively is key to getting the most out of the Free Tier. One of the biggest challenges is understanding when free tier limits are exceeded and what happens next. Here are best practices and tools to help users manage their AWS Free Tier effectively:
- Verify Free Tier Eligibility: Each AWS service comes with unique limits. For example, Amazon S3 offers 5 GB of standard storage for the first 12 months. Verify service limits before utilizing them to ensure they fall under Free Tier eligibility.
- Viewing Active AWS Resources: The AWS Billing Console is your go-to tool for viewing resource usage. From the Billing console, users can navigate to the Free Tier section to verify which services are being used under the free tier and what their current usage is. For instance, if you see that an EC2 instance is incurring charges in the Ohio region, you can take steps to manage those resources appropriately.
- Transitioning Out of Free Tier: When the free period ends or the usage exceeds the limits, users can either terminate the AWS resources or transition to paid services. The AWS Pricing Calculator is an excellent tool for estimating potential costs when continuing beyond the free tier.
By verifying usage regularly and understanding what incurs charges, users can make informed decisions to avoid unexpected bills.
AWS Free Tier Introduction to Managing Services
Monitoring AWS Free Tier Services
Monitoring AWS Free Tier usage is crucial for avoiding unforeseen expenses. AWS provides multiple tools to help track and manage costs effectively.
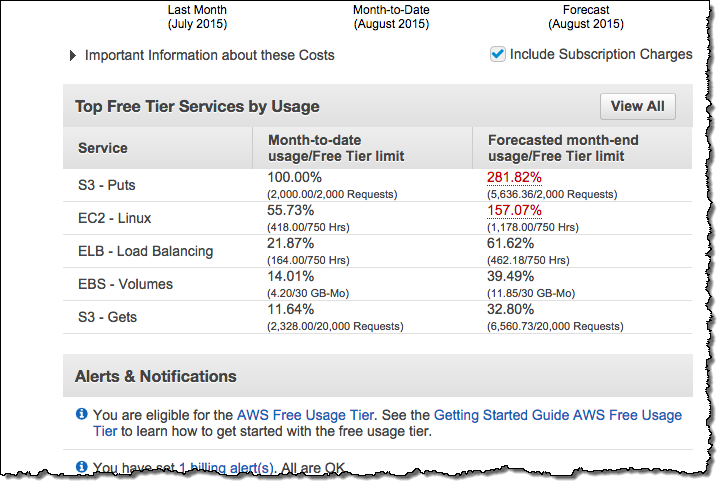
- AWS Billing Console: The Billing Console is a great starting point for monitoring your service usage. By selecting Free Tier from the navigation pane, users can see detailed insights about how much of their free tier limit has been utilized. For instance, you can see whether you are approaching the limit of 750 hours for an EC2 instance.
- AWS Budgets: AWS Budgets allows users to set custom cost alerts for free tier usage. For example, a Zero Spend Budget can notify you via email when your spending exceeds the free tier limit. This proactive approach ensures you know when you are about to incur costs. Additionally, the Monthly Spend Budget template can help you control overall spending by alerting you when you reach certain thresholds, such as $20 per month.
- AWS Cost Explorer: AWS Cost Explorer is another useful tool, offering detailed cost and usage visualizations. It helps identify cost drivers, usage trends, and even anomalies, making it invaluable for teams looking to manage costs across multiple AWS accounts.
Setting up these monitoring tools helps users take full control of their cloud expenses while exploring the AWS ecosystem through the Free Tier.
AWS Free Tier Introduction to Monitoring Services
The AWS Free Tier offers an excellent opportunity for developers, students, and enterprises to get hands-on with AWS services at no cost, but managing and monitoring usage is crucial to keep it free. By understanding the types of free tier offerings, managing services effectively, and using monitoring tools like AWS Budgets and AWS Cost Explorer, users can optimize their cloud journey without the worry of surprise costs.
Whether you’re building a new application, testing existing workloads, or gaining new skills, AWS Free Tier services provide a flexible and affordable gateway into cloud computing. Start with tools like the AWS Pricing Calculator and AWS Cost Explorer to keep a handle on your usage and costs, ensuring a seamless transition when your Free Tier period ends.
Ready to begin your journey? Head over to the AWS Free Tier homepage and start experimenting today!
For more information about how to monitor your free tier usage, see the following resources:
- Managing your costs with AWS Budgets in the AWS Billing and Cost Management User Guide
- Tracking your AWS Free Tier usage in the AWS Billing and Cost Management User Guide
- Creating a cost budget in the AWS Billing and Cost Management User Guide
- Announcement: 1-Click templates and tutorials in AWS Budgets