Arithmetic Operators in Python
In this post, we explore the various arithmetic operators available in Python. You’ll learn how to use addition, subtraction, multiplication, and more to perform calculations. We’ll also look at how to work with variables to create dynamic operations.
What are Arithmetic Operators?
In Python, arithmetic operators are symbols that represent mathematical operations. They allow you to perform basic calculations like addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division, as well as more advanced operations like exponentiation and finding remainders.
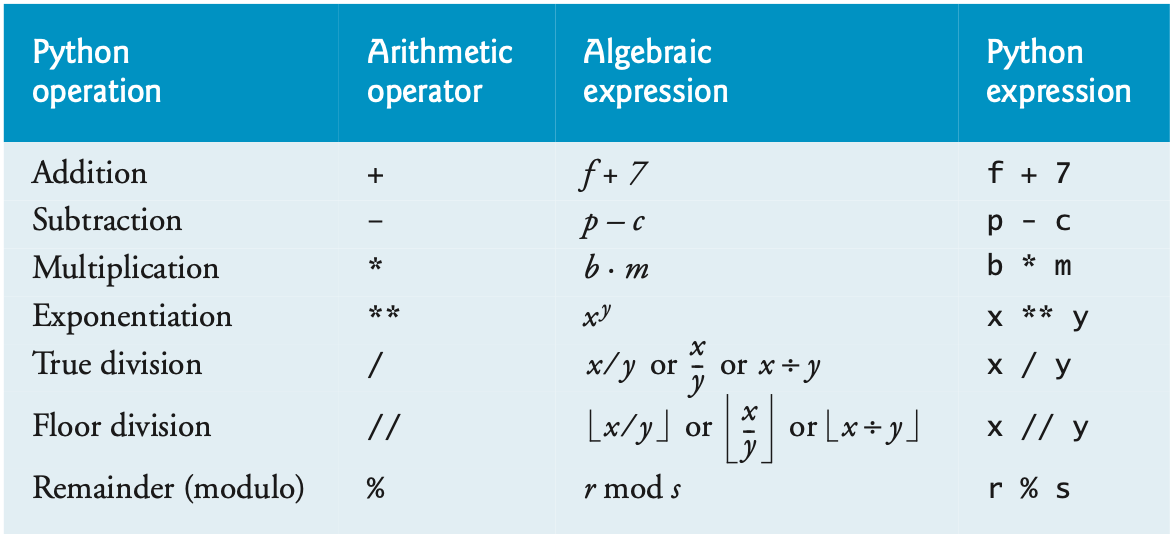
Common Arithmetic Operators in Python
- Addition (
+): Adds two numbers.1 2 3 4
a = 10 b = 5 sum_result = a + b print(f"Sum: {sum_result}") # Output: Sum: 15
- Subtraction (
-): Subtracts the second number from the first.1 2 3 4
a = 10 b = 5 difference = a - b print(f"Difference: {difference}") # Output: Difference: 5
- Multiplication (
*): Multiplies two numbers.1 2 3 4
a = 10 b = 5 product = a * b print(f"Product: {product}") # Output: Product: 50
- Division (
/): Divides the first number by the second and returns a float.1 2 3 4
a = 10 b = 5 division = a / b print(f"Division: {division}") # Output: Division: 2.0
- Modulo (
%): Returns the remainder of the division of the first number by the second.1 2 3 4
a = 10 b = 3 modulo = a % b print(f"Modulo: {modulo}") # Output: Modulo: 1
- Exponentiation (
**): Raises the first number to the power of the second.1 2 3 4
a = 2 b = 3 exponent = a ** b print(f"Exponent: {exponent}") # Output: Exponent: 8
- Floor Division (
//): Divides the first number by the second and rounds down to the nearest whole number.1 2 3 4
a = 10 b = 3 floor_division = a // b print(f"Floor Division: {floor_division}") # Output: Floor Division: 3
Using Arithmetic Operators with Variables
Arithmetic operators become especially powerful when used with variables. Instead of being limited to static numbers, you can store values in variables and perform operations dynamically:
1
2
3
4
num1 = 15
num2 = 4
sum_result = num1 + num2
print('Sum: ', sum_result) # Output: Sum: 19
By using variables, you can manipulate your data and create more flexible programs.
Precedence of Arithmetic Operators
Just like in mathematics, Python follows a hierarchy when evaluating expressions with multiple operators, known as the order of precedence:
- Parentheses: Operations within parentheses are executed first.
- Exponentiation (
**): This operator has the next highest precedence. - Multiplication, Division, Floor Division, and Modulo (
*,/,//,%): These operators share the same level of precedence. - Addition and Subtraction (
+,-): These operators have the lowest precedence.
For example:
1
2
3
4
5
a = 10
b = 5
c = 2
result = a + b * c ** 2 / (b - c)
print(f"Result: {result}")
In the above code, Python evaluates the expression in the following order:
- Exponentiation:
c ** 2 - Parentheses:
(b - c) - Multiplication and Division:
b * (result of c ** 2)andresult of multiplication / result of parentheses - Addition:
a + (result of division)
Practice Exercises
Try your hand at the following exercises to reinforce your understanding:
Exercise 1
Write a program that calculates the result of the following arithmetic operation: (7 + 2 / 8 - 2)**2. Use parentheses to control the order of operations.
Exercise 2
A bookstore needs to calculate the total weight of an order. Books weigh 500g each, and magazines weigh 300g each. Write a program that calculates the total weight of an order consisting of 3 books and 2 magazines.
1
2
3
4
5
6
BOOK_WEIGHT = 500
MAGAZINE_WEIGHT = 300
order_books = 3
order_magazines = 2
total_weight = (BOOK_WEIGHT * order_books) + (MAGAZINE_WEIGHT * order_magazines)
print(f"Total weight: {total_weight}") # Output: Total weight: 2100
More Information
Arithmetic operators are a fundamental part of Python and will be used frequently in almost every program you write. Understanding how to use them properly is essential for success in Python programming.
For more details on Python operators, check out:
Next Steps: In the next post, we’ll dive deeper into Text Strings. Continue learning and practicing to master these essential skills in Python!